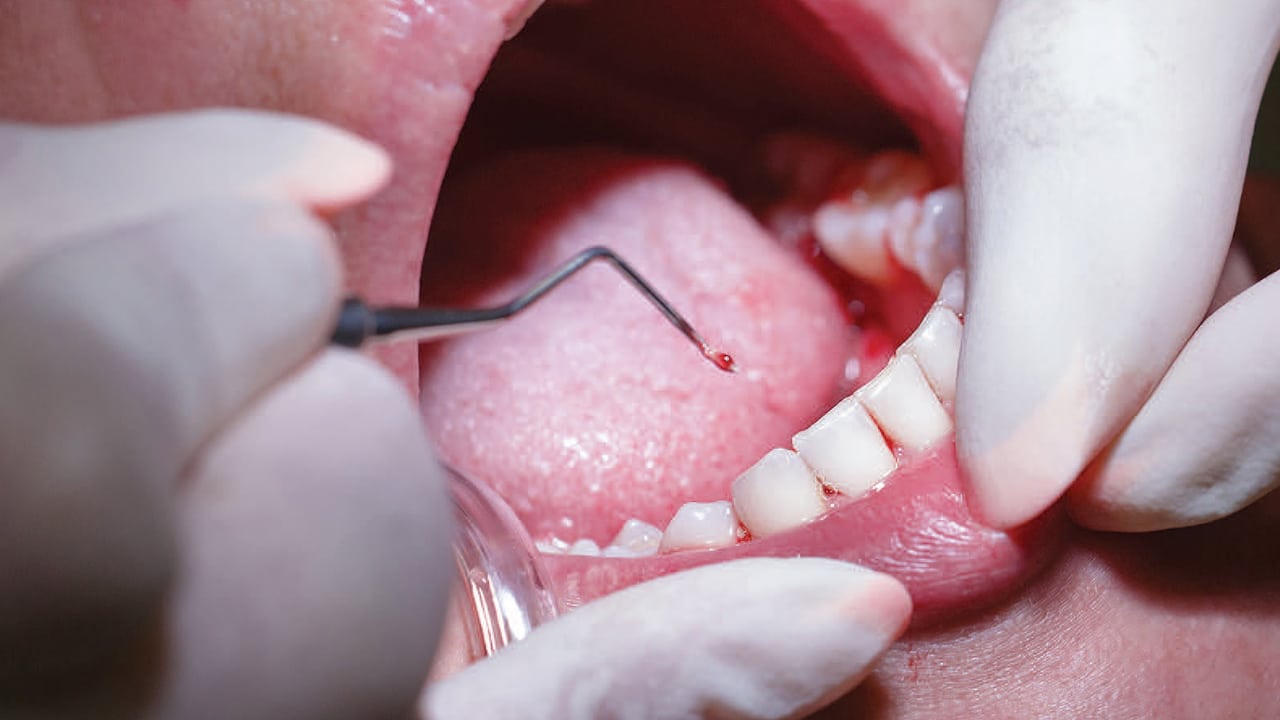
Periodontal disease affects millions of people worldwide. If this oral issue is left untreated, it can lead to –
- Gum inflammation
- Tooth loss
- Systemic health problems
Conventional treatments often involve –
- Scaling
- Root canal
- Dental implants
- Surgical interventions
However, an innovative approach gaining traction in periodontal therapy is Plasmolifting. This non-invasive procedure utilizes platelet-rich plasma (PRP) to promote tissue healing and regeneration.
A step-by-step guide to Plasmolifting in periodontal disease therapy
1. Step 1: Patient Evaluation
A thorough patient evaluation is the first crucial step in Plasmolifting for periodontal disease therapy. It involves a comprehensive assessment of the patient’s oral health, including –
- The severity of periodontal disease
- The presence of gum pockets
- Tooth mobility
- Bone loss
Also, medical history and any contraindications are reviewed to ensure you are eligible for the procedure.
2. Step 2: Informed Consent
Before proceeding, the dentist or periodontist obtains informed consent from the patient. This involves –
- Explaining the procedure
- Potential risks
- Benefits
- Expected outcomes
Ensure that you have total information and are comfortable with the therapy. Never hesitate to clarify your concerns before giving consent.
3. Step 3: Blood Collection
Plasmolifting relies on PRP derived from the patient’s blood. A small quantity of the patient’s blood (usually 10-20 milliliters) is drawn, typically from the arm, to collect PRP. This blood sample is then processed to isolate the platelet-rich plasma.
Make sure that high-quality PRP tubes are used in the process. Poor PRP tubes can impact PRP preparation sterility. Plasmolifting World offers premium quality PRP tubes in Germany at affordable rates. It was founded by a biomedical research group in 2003. The healthcare company adheres to the EU’s regulatory compliance associated with the manufacturing of medical devices.
4. Step 4: Centrifugation
The blood sample is positioned in a centrifuge, which spins it at a high speed. Centrifugation separates the blood into its constituent components –
- Red blood cells
- Platelet-rich plasma
- Platelet-poor plasma
The PRP layer is carefully extracted for use in the treatment.
5. Step 5: Local Anesthesia
Local anesthesia allows numbing the treatment area to ensure patient comfort during the procedure. This reduces any potential pain or discomfort associated with the Plasmolifting process.
6. Step 6: PRP Application
The isolated PRP, rich in growth factors and cytokines, is applied directly to the affected periodontal tissues. Syringes or other specialized delivery methods also help to introduce plasma into the gum pockets. The growth factors in PRP –
- Stimulates tissue repair
- Reduces inflammation
- Promotes the regeneration of damaged gum and bone tissue
7. Step 7: Post-Procedure Care
After the PRP application, the dentist gives patients post-operative instructions. These instructions may include recommendations for –
- Oral hygiene practices
- Dietary restrictions
- Follow-up appointments to monitor progress
8. Step 8: Monitoring and Follow-Up
Periodontal disease therapy using Plasmolifting often requires multiple sessions to achieve optimal results. The dentist closely monitors the patient’s progress during follow-up visits. The dentist or periodontist may assess –
- changes in gum pocket depth
- Tissue healing
- Overall oral health to determine the success of the treatment
Conclusion
Plasmolifting in periodontal disease therapy offers a promising alternative to conventional treatments. Plasmolifting can promote tissue healing and improve the outcomes of periodontal disease therapy by feeding the regenerative potential of platelet-rich plasma.
Only qualified and experienced dental professionals must perform this procedure to ensure its safety and effectiveness.